The AMaCC Platform team supports all the CEISAM’s researchers in their organic chemistry, materials chemistry and isotope analysis projects.
We provide academic and industrial partners with high-performance tools for the isolation and characterization of a broad spectrum of molecules.
We offer our expertise in the following fields:
The platform has different techniques to help in the structural identification of molecules:
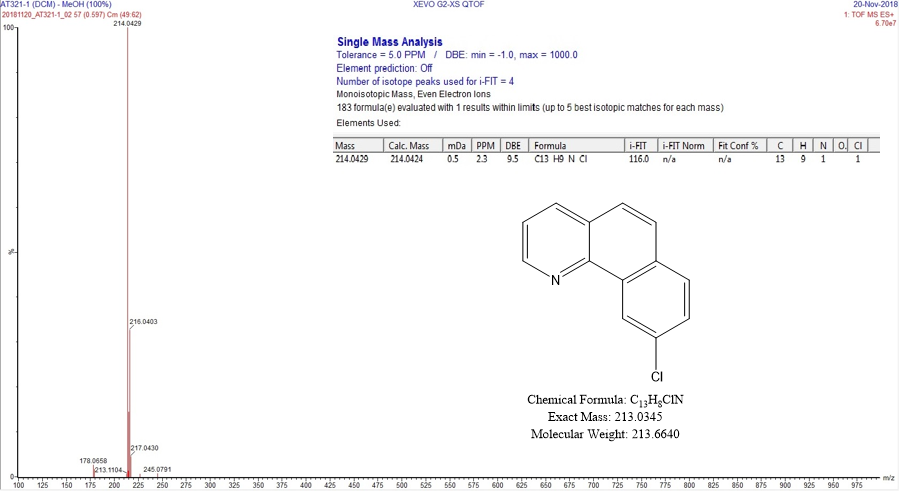
- Exact mass measurement in high resolution ESI, APCI, ASAP (solid introduction probe) of parent ions;
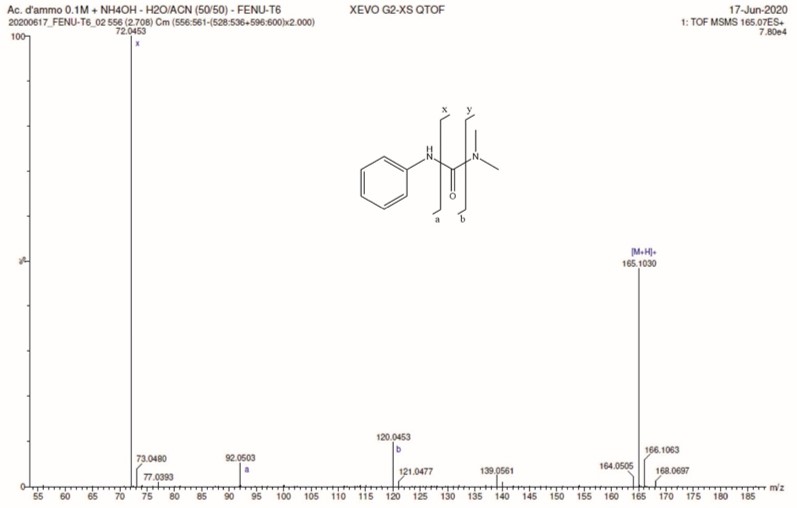
- MS² with high-resolution accurate mass measurement of fragment ions;
- GC-MS (electronic ionization) with database search (NIST).
HPLC and UPLC are coupled to various detectors (UV, ELSD and MS). This enables the characterization of complex mixtures or the relative purity’s. determination.
- The UV detector is used for the analysis of pure compounds or complex mixtures with chromophores
- The Evaporation Light Scattering Detector (ELSD), a quasi-universal detector, enables the analysis of all the constituents present in a mixture (except very volatile compounds). It’s compatible with the gradient mode ;
- The mass spectrometers (simple quadrupole and Q-Tof) give the nominal mass of the mixture’s compounds which are ionized ;
- The high-resolution mass spectrometer (Q-Tof) gives the exact mass of the compounds with proposals of molecular formulas for for the parent ion and its fragments (if an MS² analysis is implemented).
GC instruments are coupled to a flame ionization detector (FID) or to a simple quadrupole mass spectrometer. They offer the possibility to analyze complex mixtures in order to characterize the molecules present or to determine a relative purity (subject to the volatility and thermal resistance of the analyzed molecules).
The coupling with the simple quadrupole mass spectrometer gives the nominal mass of the compounds of the mixture which are ionized.
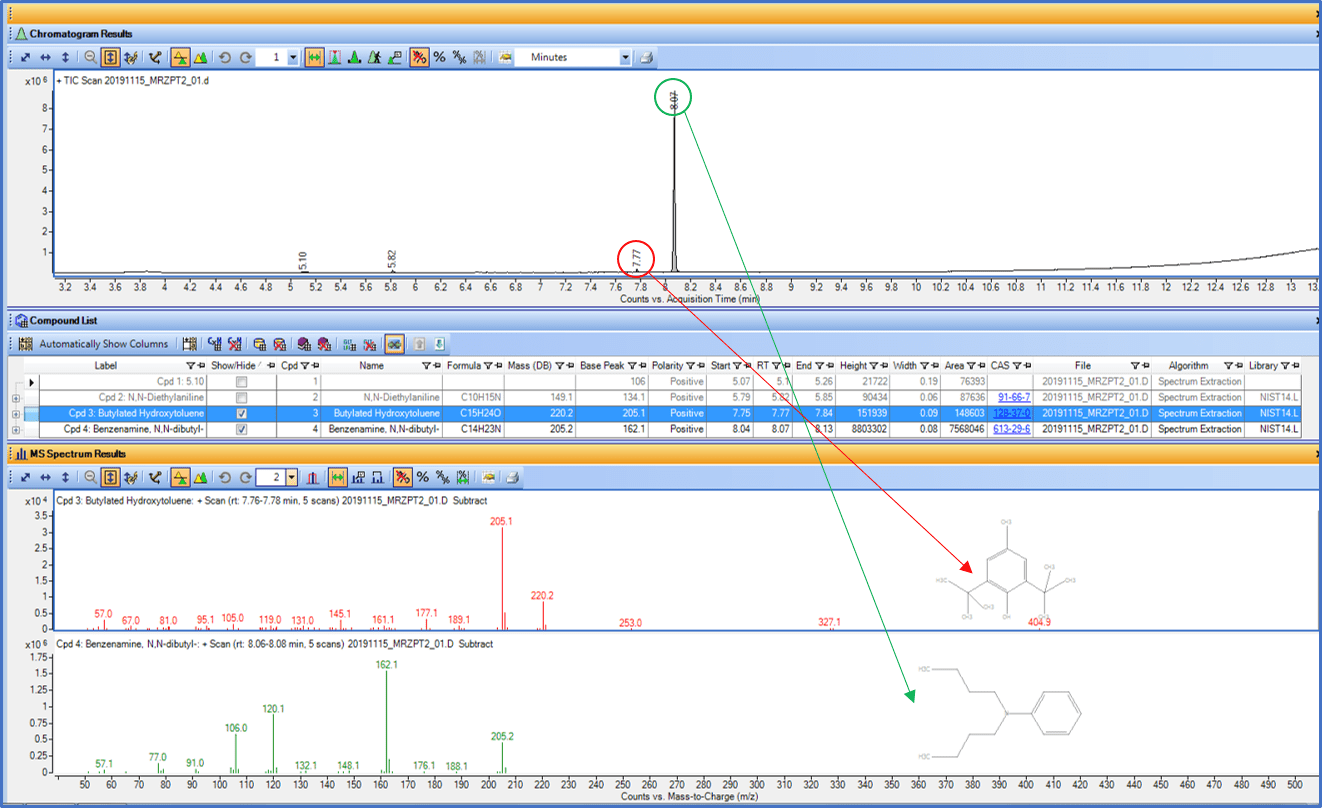
Within the framework of interdisciplinary projects, we offer our expertise for quantitation and preparation of samples of a wide spectrum of molecules from biological matrices, materials or nanoparticles.
For this purpose the platform has several techniques at its disposal:
- GC-FID, "universal" detector
- GC-MS, accessible mass range: 50 to 650 Da
- HPLC-PDA (diode-array UV), wavelength range 190 to 800 nm
- HPLC-MS (single quadrupole), accessible mass range: 30 to 1250 Da
- UPLC PDA, wavelength range 190 to 800 nm
- UPLC-DEDL,"universal" detector, compatible with the gradient mode
We have a large set of columns in normal phase, inverse C18, HILIC, mixed mode (inverse phase / anion exchange) allowing us various separations. The platform develops robust and specific quantitation methods for the desired molecules.
Example of quantitative analysis of small organic molecules
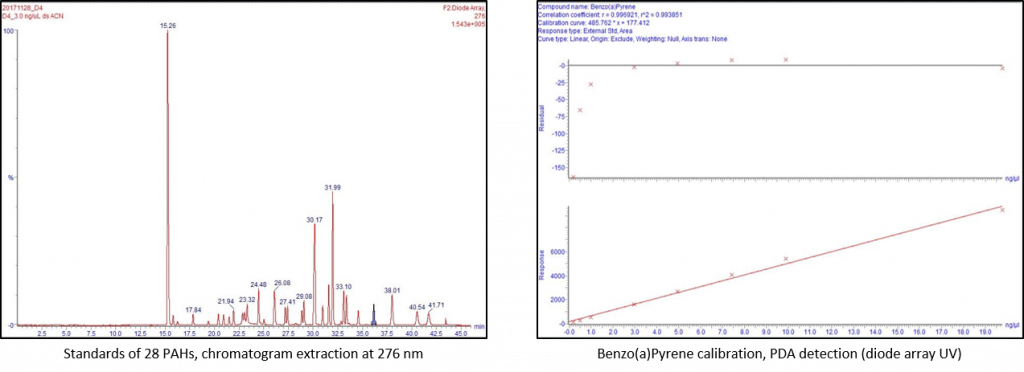
Quantitation of 28 PAHs extracted from bitumen fumes by HPLC-UV:
Quantitative kinetic monitoring of an enzymatic reaction:

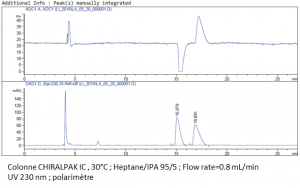
We have an HPLC dedicated to the analysis of chiral compounds. It is equipped with a diode-array UV detector (DAD1100, Agilent) and a polarimeter (OR2090, JASCO). This double detection enables the measurement of the enantiomeric excess as well as the sign of the majority enantiomer. We have nine chiral columns to screen on a wide range of molecules:
- CHIRALPAK AD-H, AS-H, IA, IB, IC ;
- CHIRALCEL OD-H, OJ-H ;
- Lux Amylose-2 ;
- Lux Cellulose-4.
For any chiral analysis request, a purity analysis as well as a racemic analysis are required.